Without any further words we give all the puzzles and our short solutions to each of them. To see the solutions, select the text in your browser (e.g. by dragging the mouse).
Puzzle ID: birds Ten birds sit on a clothes line. We shoot and kill one of them. How many birds remain on the clothes line? The answer for this puzzle consists of two lines, containing respectively: - the ID of this puzzle - one number: the number of birds that remain on the clothes line
Puzzle ID: bus A bus was travelling with less than 100 passengers. At stop A, exactly three quarters of the passengers got off and 7 passengers got on the bus. The same thing happened at next two stops, B and C. How many people got off at the stop C? The answer for this puzzle consists of two lines, containing respectively: - the ID of this puzzle - the number of people getting off at C
Puzzle ID: palindrome Suppose we write dates in the MMDDYYYY format. In this format, the 2nd of October 2001 is a palindrome (a string equal to its reverse): 10022001. Find the previous date that yields a palindrome in this format. The answer for this puzzle consists of two lines, containing respectively: - the ID of this puzzle - the 8-digit string
Puzzle ID: bicycle A bicycle stands on a straight road. A piece of string is attached to its rear wheel as shown in the image:

Suppose that we slowly start to pull the string to the left. What will happen to the bicycle? A) It will start moving to the left. B) It will start moving to the right. C) It will stay in the same place. Assume that the wheel of the bicycle doesn't slip on the ground (i.e. whenever the bicycle moves, the wheel has to rotate). Also assume that the bicycle stays in an upright position all the time. The answer for this puzzle consists of two lines, containing respectively: - the ID of this puzzle - the uppercase letter corresponding to the correct answer
Puzzle ID: cube You have a cube NxNxN. How many straight cuts are necessary to cut it into N^3 cubes of size 1x1x1? You may arrange the pieces in any way you like before making each cut. a) Solve for N=3 b) Solve for N=4 The answer for this puzzle consists of three lines, containing respectively: - the ID of this puzzle - the number of cuts from part a) - the number of cuts from part b)
Puzzle ID: girl1 In a two-child family, one child is a boy. What is the probability that the other child is a girl? The answer for this puzzle consists of two lines, containing respectively: - the ID of this puzzle - the answer in the form a/b (where a,b are relatively prime)
Puzzle ID: girl2 In an unnamed overpopulated country the rulers agreed on a new law: Each woman may have as many children as she wants to, until she gives birth to a girl. After that, she may have no more children. Assume that the law will never be broken. All families will have as many children as they are (physically and legally) able to. On each birth either one boy or one girl is born with equal chances. In the current population the ratio males:females is 1:1. What will happen in the next 100 years? A) The ratio of males to females will go up B) The ratio of males to females will stay the same C) The ratio of males to females will go down The answer for this puzzle consists of two lines, containing respectively: - the ID of this puzzle - the uppercase letter corresponding to the correct answer
Puzzle ID: statements
Given is a list with 2004 statements:
1. Exactly one statement on this list is false.
2. Exactly two statements on this list are false.
3. Exactly three statements on this list are false.
...
2004. Exactly 2004 statements on this list are false.
a) Determine which statements are true.
b) Replace "exactly" by "at least". Again, determine which statements are true.
The answer for this puzzle consists of three lines, containing respectively:
- the ID of this puzzle
- the encoded answer from part a)
- the encoded answer from part b)
How to encode the answer? If no statements are true, write the word 'NONE'
(without the quotes). Otherwise take the set of true statements and write it
as a set of ranges. E.g. the set {1,2,3,7,9,100,101} is encoded as
1-3,7,9,100-101
Puzzle ID: letters How many letters does the _shortest_ correct answer to this puzzle contain? The answer for this puzzle consists of two lines, containing respectively: - the ID of this puzzle - your exact answer
Puzzle ID: century The twentieth century ended on 31. 12. 2000, which was a Sunday. Looking into the future, on which days of the week won't any century ever end? Remember that leap years are those divisible by 400 plus those divisible by 4 but not by 100. (1996 was a leap year, so was 2000, but 2100 won't be a leap year and neither will 2047.) The answer for this puzzle consists of two lines, containing respectively: - the ID of this puzzle - the days of the week on which no century will ever end The exact form of the answer is a comma-separated list of three-letter abbreviations of the days in the order in which they appear in a week. E.g. if the answer were Monday, Tuesday and Wednesday, write the string 'Mon,Tue,Wed' (without the quotes).
Puzzle ID: 1000robbers One thousand robbers meet in their hideout and plan to divide all the loot they stole. All robbers value their life above everything. They are smart, greedy (want as much loot as possible) and bloodthirsty (given two different outcomes with the same payoff for a robber, he prefers the one where more other robbers die). They all know this information. The robbers agreed that every day they will take a vote. If at least 50% of the robbers vote to split the loot, everybody takes a fair share and leaves the hideout. Otherwise the currently youngest robber is shot. How many robbers will survive? In the last round of voting, how many of them will vote for splitting the loot? (Assume that if a robber knows that his vote doesn't matter, he votes against splitting the loot.) The answer for this puzzle consists of three lines, containing respectively: - the ID of this puzzle - the number of robbers that survive - the number of robbers that voted to split the loot in the last round
Puzzle ID: wires Imagine that you are an electrician. You are called to a very high tower, because their lifts are broken. When you arrive, you find that the lifts were sabotaged: 2005 wires were cut and now all of them hang from the top of the tower down to its bottom. (I.e. each of the wires has got one loose end near the bottom of the tower and one loose end near its top.) Before you can proceed with the repairs, you need to identify all the matching ends of the wires. For each of the bottom ends you have to know its corresponding end at the top. Your only instrument is a simple probe -- a battery and a bulb. If you attach two ends of wires to this probe, the bulb lights up if and only if the other ends of these two wires are currently conductively connected (maybe through one or more other wires). At each end of the tower you may connect and disconnect the ends of wires in an arbitrary way. Since the tower is so high, you want to minimize the number of times you have to climb up and down the staircase, regardless of how much work you have to do while you are at the top or bottom. What is the minimum number of traversals required? (Once up and down counts as 1.) The answer for this puzzle consists of two lines, containing respectively: - the ID of this puzzle - the minimal number of traversals
Puzzle ID: chess Given is a game of chess in progress. Your task is to determine which were the last two pieces that moved before the current position was reached. The current position:
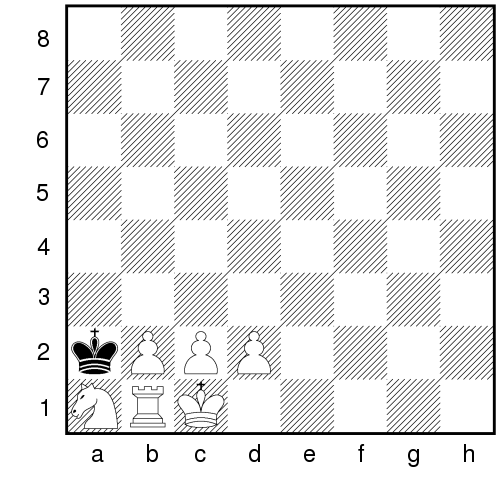
white: king on c1, rook on b1, knight on a1, pawns on b2, c2, d2
black: king on a2
The answer for this puzzle consists of four lines, containing respectively:
- the ID of this puzzle
- the color of the player that moved the last piece
('white' or 'black', without the quotes)
- the last move made by this player before the position was reached
- the last move made by the other player
Enter both moves in standard chess notation. (Assume that no piece was captured
in the move the other player made.)
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
Explanation of the chess notation [a subset you need to know]:
A move is written as [piece][x](destination square).
The piece is represented by an uppercase letter: King Queen Rook kNight Bishop
If no piece is specified, the moving piece is a pawn. The optional x means the
moving piece has captured an opponent's piece. A lowercase letter is used to
specify the row of the destination square:
Examples:
- a king moves from e4 to e5: Ke5
- a knight moves from d4 to f3, taking an opponent's rook: Nxf3
- a pawn moves from g2 to g4: g4
Puzzle ID: 24 From the numbers 1, 3, 4 and 6 create an expression giving the result 24. You may use only parentheses and the operations +, -, * and /. You have to use each of the given four numbers exactly once. The answer for this puzzle consists of two lines, containing respectively: - the ID of this puzzle - the expression (no spaces, no unnecessary parentheses)
Puzzle ID: product The sum of some (not necessarily distinct) positive integers is 34. What is the greatest possible value of their product? The answer for this puzzle consists of two lines, containing respectively: - the ID of this puzzle - the greatest possible product
Puzzle ID: cannibals 47 people were capured by cannibals. For some obscure reason, the cannibals want to give the prisoners one last chance. They prisoners will have to stand in a line behind each other. Then the cannibals' shaman places a hat on each of the prisoners' heads. Each of these hats will be either white or black. Each prisoner can only see the colors of the hats people in front of him received. Now the shaman will ask each of the prisoners to guess the color of his hat. The first to answer is the prisoner at the end of the line (seeing all hats except for his own), then the shaman proceeds along the line. The last to answer is the prisoner at the front of the line.. If a prisoner's guess is correct, he is released immediatly, otherwise he is left to be eaten. a) Suppose that the prisoners know this procedure and that before it starts they have the time to agree on a strategy. How many of them are GUARANTEED to be saved if they find the optimal strategy? b) Solve the same task, if there are hats of 3 different colors (mauve, ochre and navy blue). The answer for this puzzle consists of three lines, containing respectively: - the ID of this puzzle - the number of saved prisoners from part a) - the number of saved prisoners from part b)
Puzzle ID: 5robbers Five robbers (Andrew, Bill, Carl, David and Wendy) want to divide loot consisting of 1000 identical diamonds. In alphabetic order they make a proposal on how to split the loot. After a proposal is announced, the robbers take a vote. If a (strict) majority agrees, the proposal is carried out and everyone goes to spend his share. If the proposal is rejected, its author is shot. All robbers value their life above everything. They are smart, greedy (want as many diamonds as possible) and bloodthirsty (given two different outcomes with the same payoff for a robber, he prefers the one where more other robbers die). They all know this information. a) How many diamonds will Andrew get, if we suppose that each proposal may only specify how many diamonds will which of the robbers get? b) How many diamonds will he get, if each proposal may also include shooting other robbers? The answer for this puzzle consists of three lines, containing respectively: - the ID of this puzzle - the number of diamonds from part a) - the number of diamonds from part b)
Puzzle ID: operation Given are the following facts: 1 + 1 = 0 2 + 2 = 0 3 + 5 = 0 6 + 8 = 3 8 + 8 = 4 9 + 7 = 1 11 + 567 = 1 How much is 680 + 369? The answer for this puzzle consists of two lines, containing respectively: - the ID of this puzzle - one number: the answer
Puzzle ID: coinseq Suppose we repeatedly throw a fair coin. Clearly the expected number of throws until we see a head is 2. The expected number of throws until we see two heads in a row is already 6. Suppose H denotes a head and T a tail. So e.g. HHT is a consecutive sequence of 2 heads and 1 tail. a) What is the expected number of throws we have to make until we observe the sequence HHHHHHH? b) ... the sequence HT? c) ... the sequence HHTHHHHHTHHHHHHTHHHHHTHHHH? The answer for this puzzle consists of four lines, containing respectively: - the ID of this puzzle - the exact result from part a) - the exact result from part b) - the exact result from part c)
Puzzle ID: ipsc We really admire you if you see this puzzle statement. We tried really hard to create a really challenging last hard puzzle. We succeeded. Not even the author managed to solve it. We present a somewhat simplified version. Question: Will you participate also in IPSC 2006? Think hard before you answer... your answer will be saved in our logs! ;) The answer for this puzzle consists of two lines, containing respectively: - the ID of this puzzle - your answer (one word, use lowercase letters only)